This library is deprecated. Google no longer supports web authentication from WebViews.
WebBasedOAuth
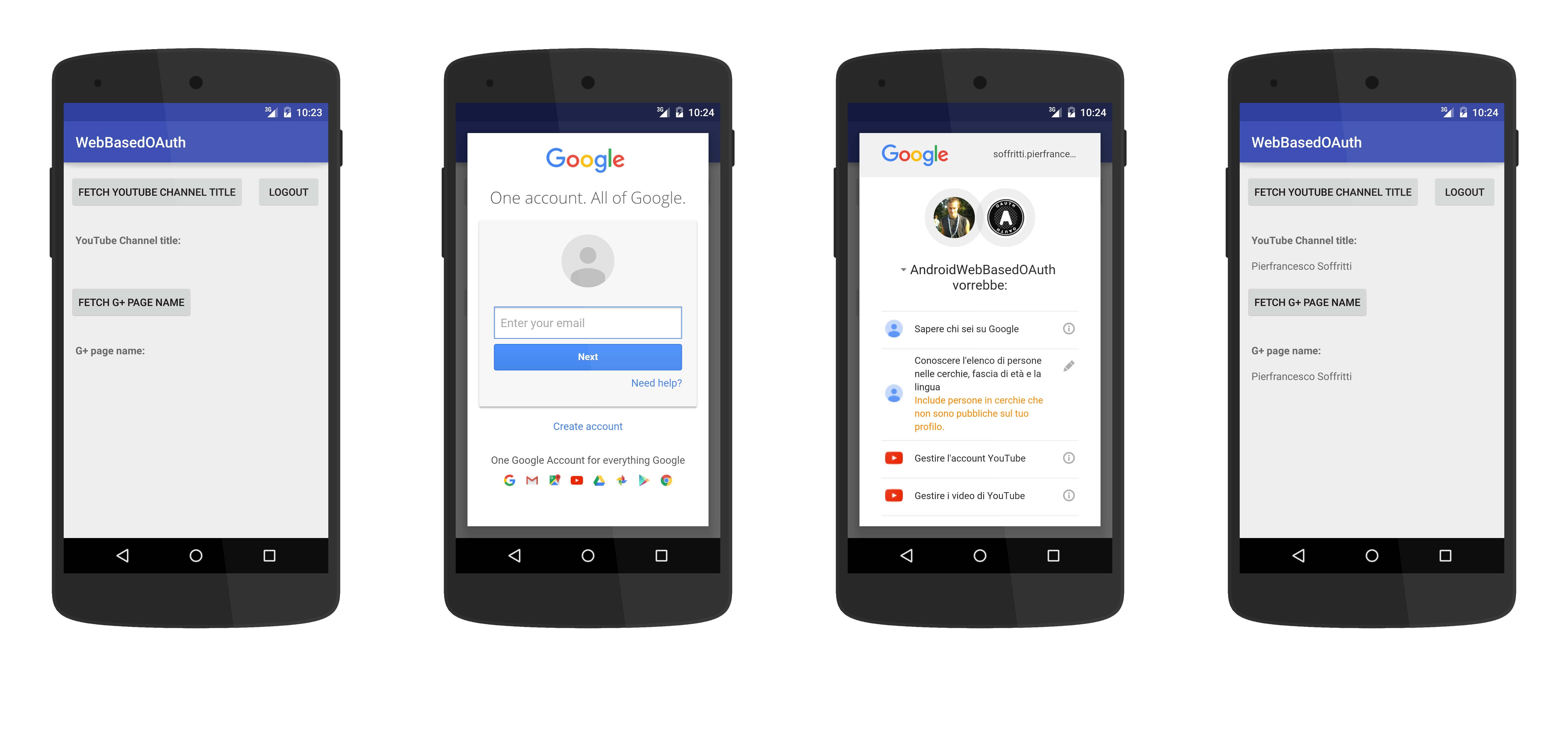
Google offers some native ways to implement OAuth authentication in Android apps, but all of them suffer of the same problem: they don't allow access to secondary accounts (also called linked accounts) and force the user to always log into his main account. This is not a problem in most cases, but for some apps can be a huge limitation. For example: YouTube allows an account to have a main channel and multiple secondary channels. Some users may use regularly the secondary channels, so if you're building an app that lets them authenticate in their YouTube channel, you must provide the option to log into both the main channel and the secondary channels. Otherwise they won't use your app.
Apparently the only way to have this basic functionality is to use the web-based OAuth process.
This library implements web-based OAuth in a simple way, in order to solve the problem illustared above.
If you don't need to access any secondary account (some Google services can't even use them) you should use the libraries provided by Google.
Download the sample app here
Apps using this library: Shuffly
Download
Add this to you project-level build.gradle:
allprojects {
repositories {
...
maven {
url "https://jitpack.io"
}
}
}
Add this to your module-level build.gradle:
dependencies {
compile 'com.github.PierfrancescoSoffritti:WebBasedOAuth:0.6'
}
Usage
Use the Authenticator class to get the access token from the server.
You must provide an implementation of CredentialPersister, needed to store the authentication credentials. The library provides an implementation based on SharedPreferences. You must also provide all the info needed to communicate with the server. See the documentation of the constructor for more info.
Authenticator authenticator = new Authenticator(activity, new SharedPreferencesCredentialPersister(context),
OAUTH_URL, scopes, REDIRECT_URI, RESPONSE_TYPE, CLIENT_ID, ACCESS_TYPE, TOKEN_URL, CLIENT_SECRET);
Use the method getAccessToken() to get an access token.
If no access token has been previously requested, this method automatically asks the user for permissions and then gets an access token from the server.
If the access token has expired, this method automatically asks for a new one.
See the documentation of the method for more info.
Once obtained, you can use the access token to make authorized API calls. Here is an example with the Google+ API, every Google service API should have the same interface.
String accessToken = authenticator.getAccessToken();
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.setAuthorization("Bearer " + accessToken);
// you can use this object to make authorized API calls Plus plus = new Plus.Builder(AndroidHttp.newCompatibleTransport(), new AndroidJsonFactory(), request -> request.setHeaders(headers))
.setApplicationName("AppName")
.build();
try {
Plus.People.Get request = plus.people().get("me");
request.setFields("displayName");
request.setKey("yourAPIKey");
Person person = request.execute();
String name = person.getDisplayName();
}
catch (Exception e) {
authenticator.handleException(e);
}
remember to always call authenticator.handleException(e);
when you make an API call using this access token. This is necessary in order to handle the case in which the user revokes the authorization.
You can see the sample app for a working implementation with the Google+ API and the YouTube Data API.