InputMask
Description
The library allows to format user input on the fly according to the provided mask and to extract valueable characters.
Masks consist of blocks of symbols, which may include:
[]— a block for valueable symbols written by user.
Square brackets block may contain any number of special symbols:
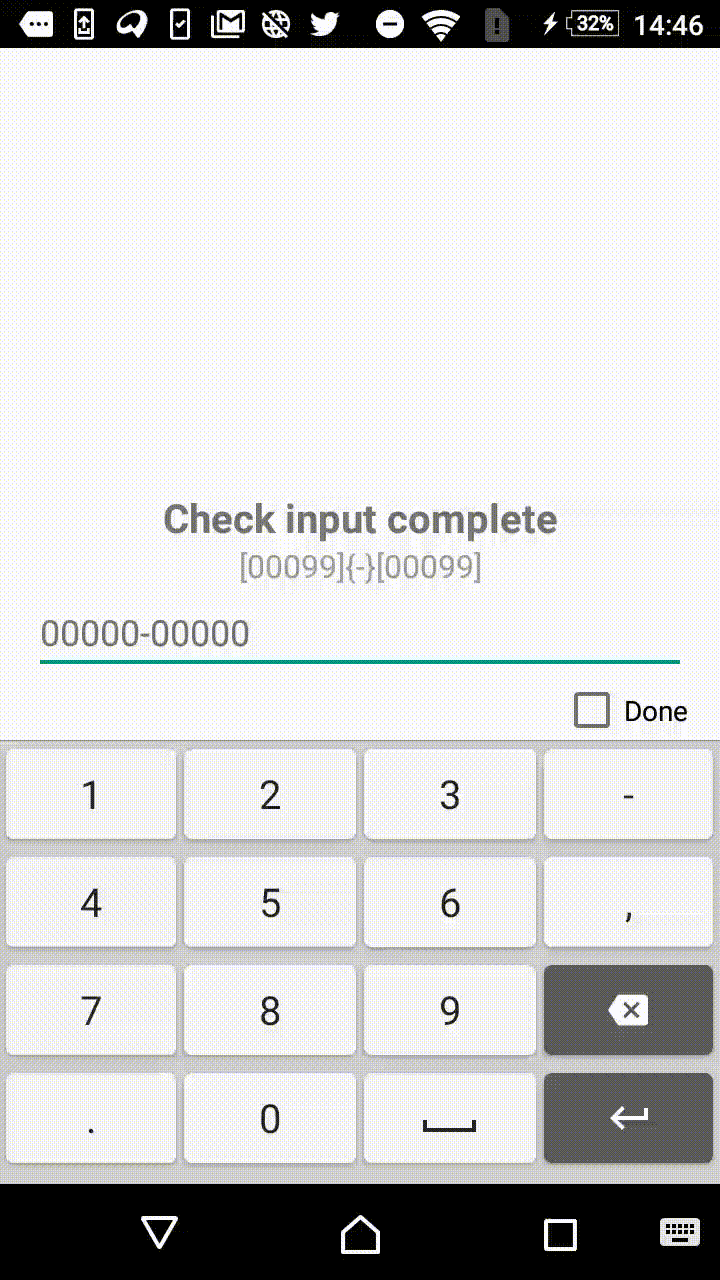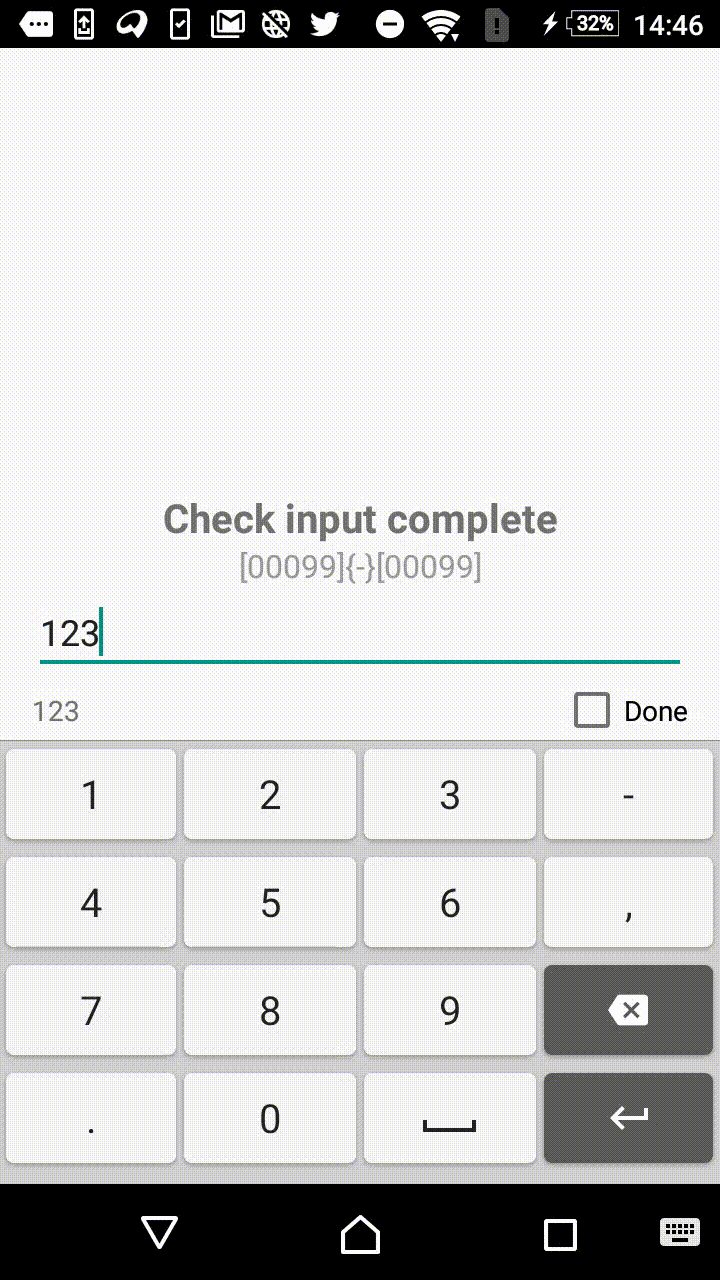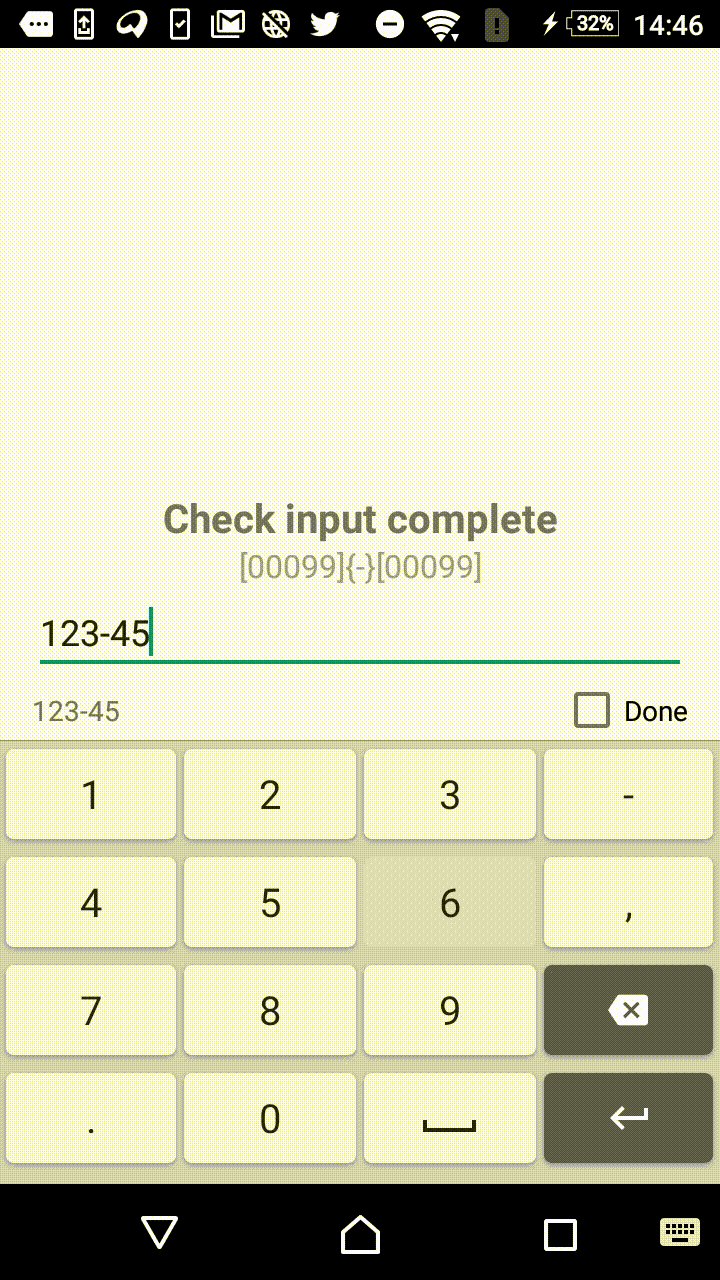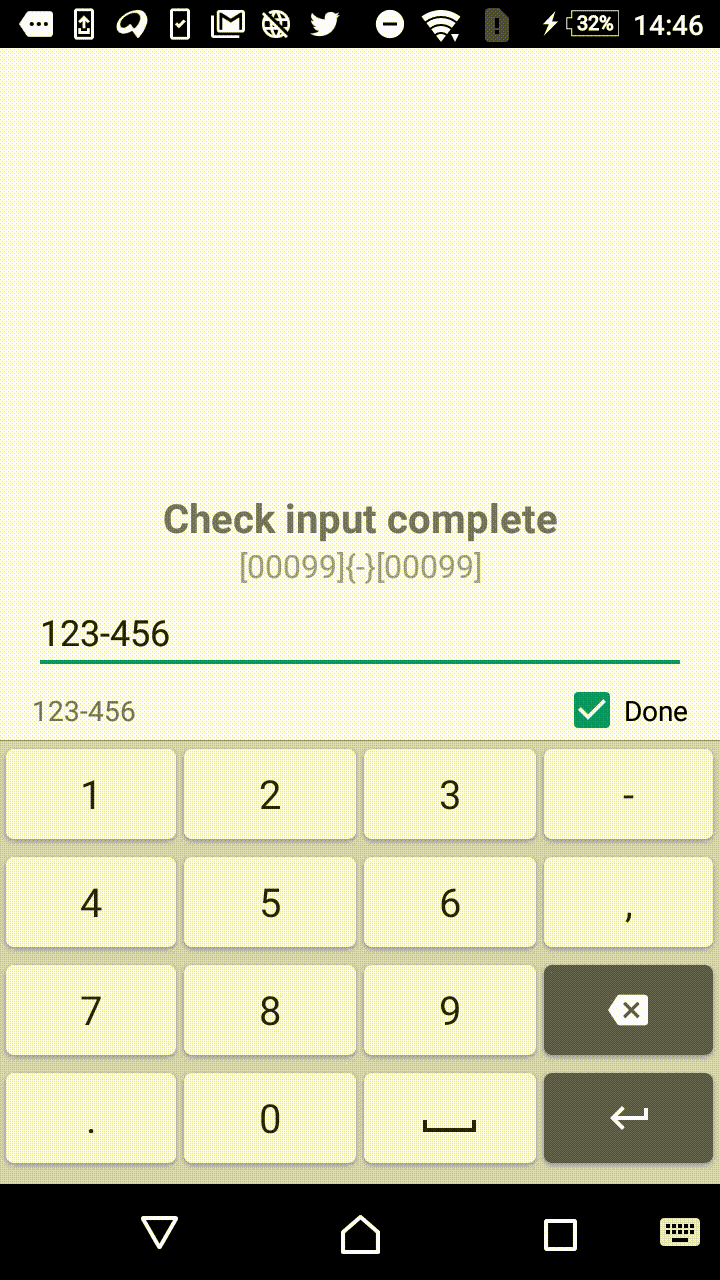
0— mandatory digit. For instance,[000]mask will allow user to enter three numbers:123.9— optional digit . For instance,[00099]mask will allow user to enter from three to five numbers.?— mandatory letter.[AAA]mask will allow user to enter three letters:abc.?— optional letter.[??????]mask will allow to enter from three to six letters._— mandatory symbol (digit or letter).-— optional symbol (digit or letter).
Other symbols inside square brackets will cause a mask initialization error.
Blocks may contain mixed types of symbols; such that, [000AA] will end up being divided in two groups: [000][AA] (this happens automatically).
Blocks must not contain nested brackets. [[00]000] format will cause a mask initialization error.
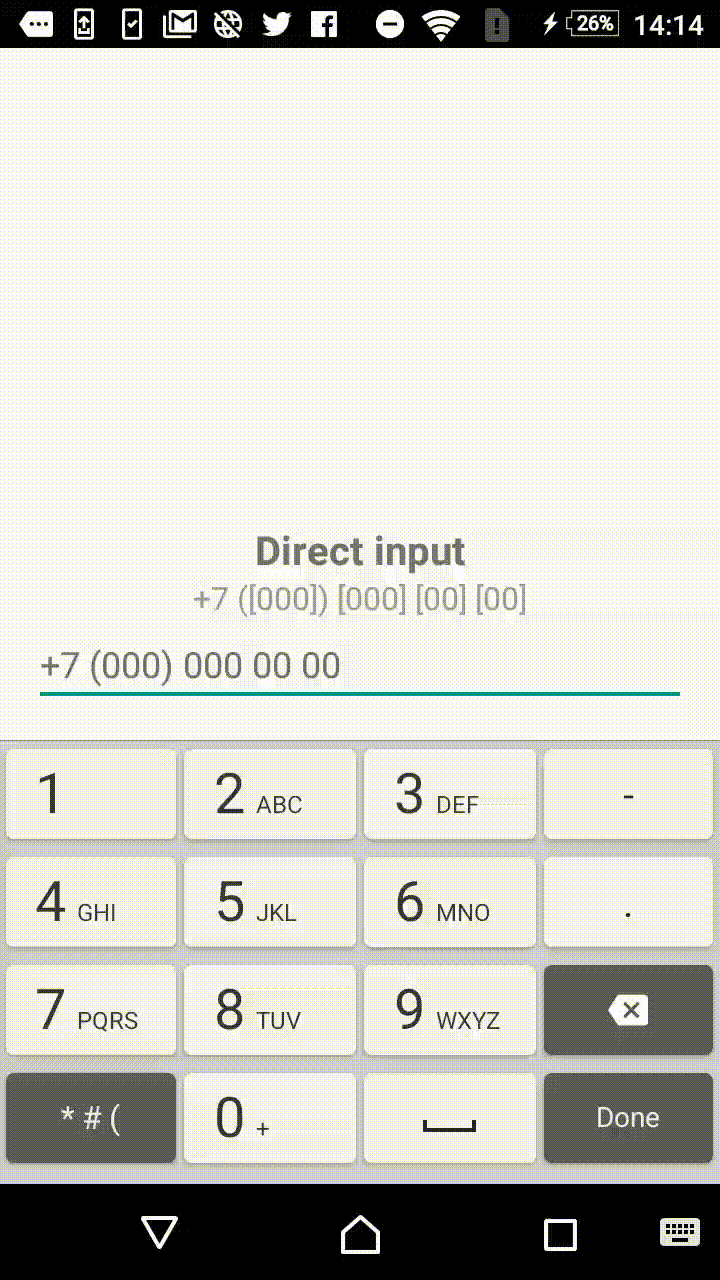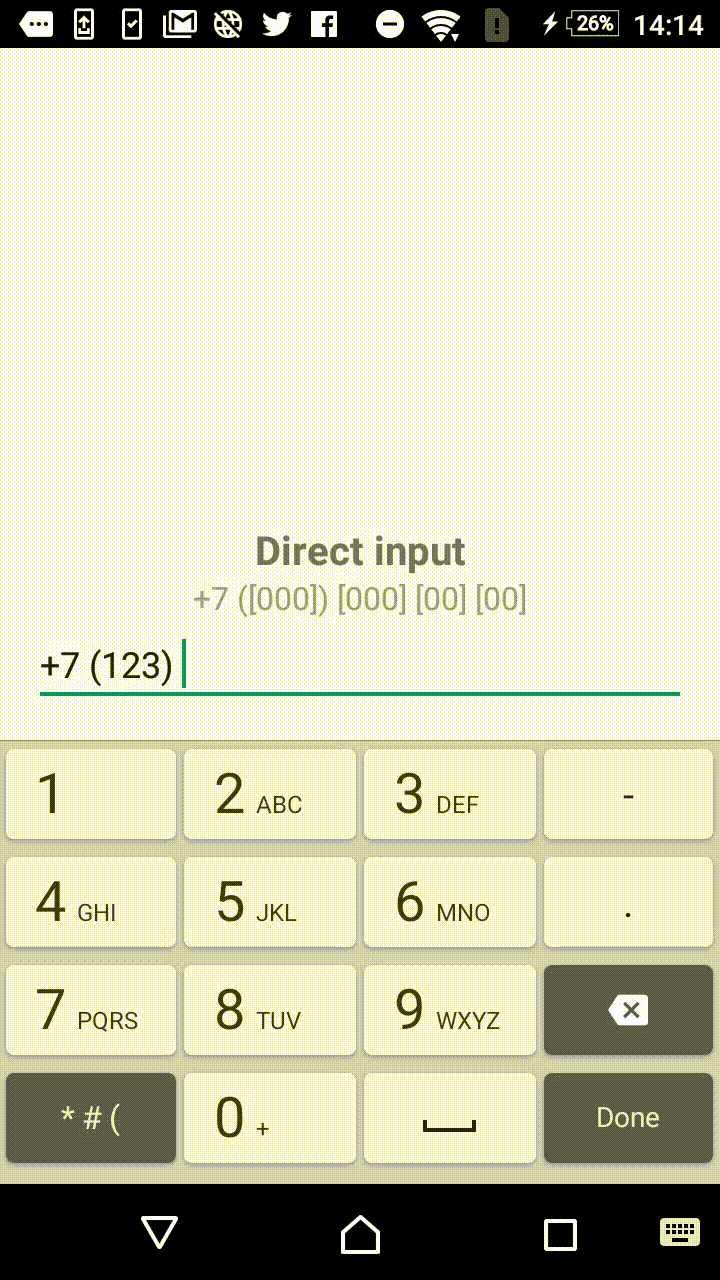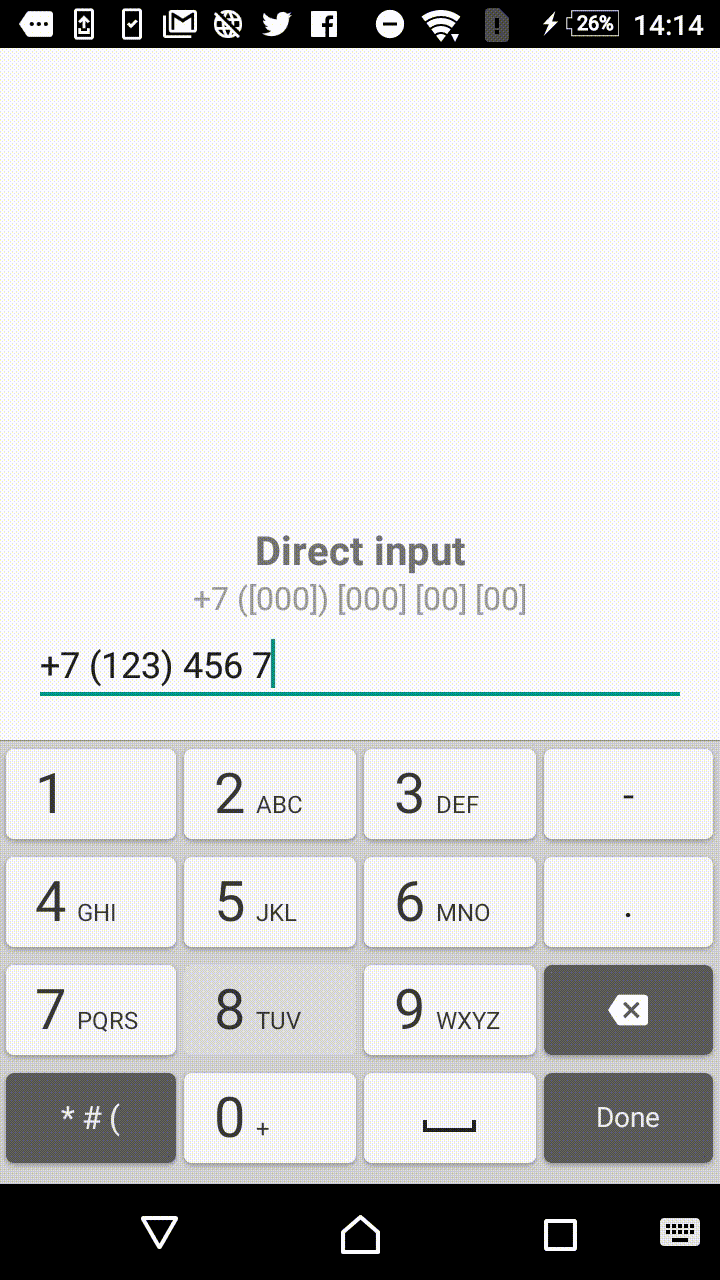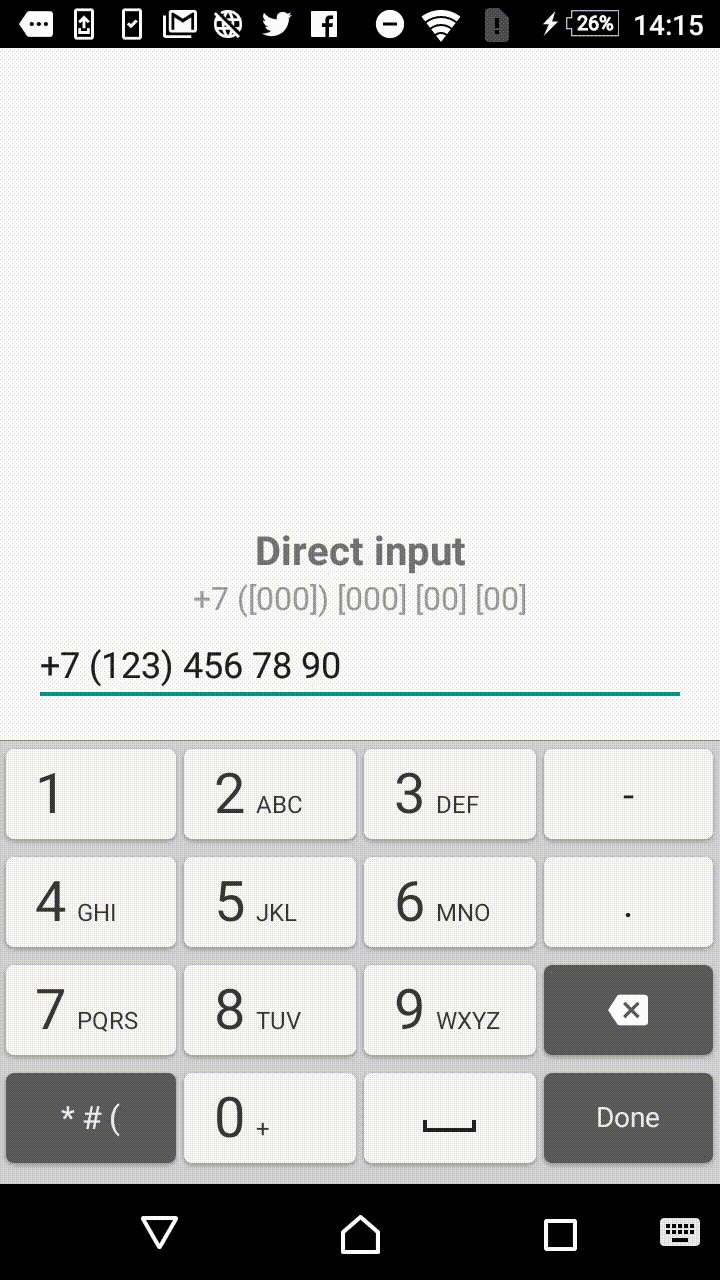
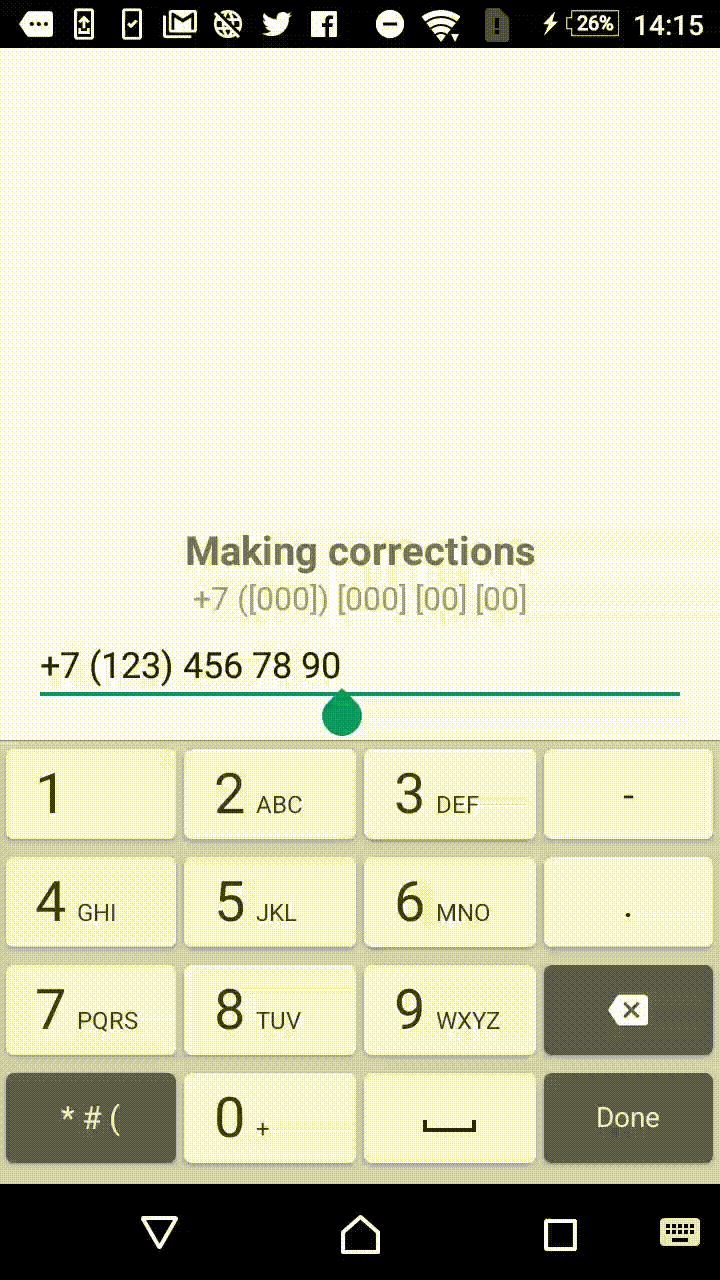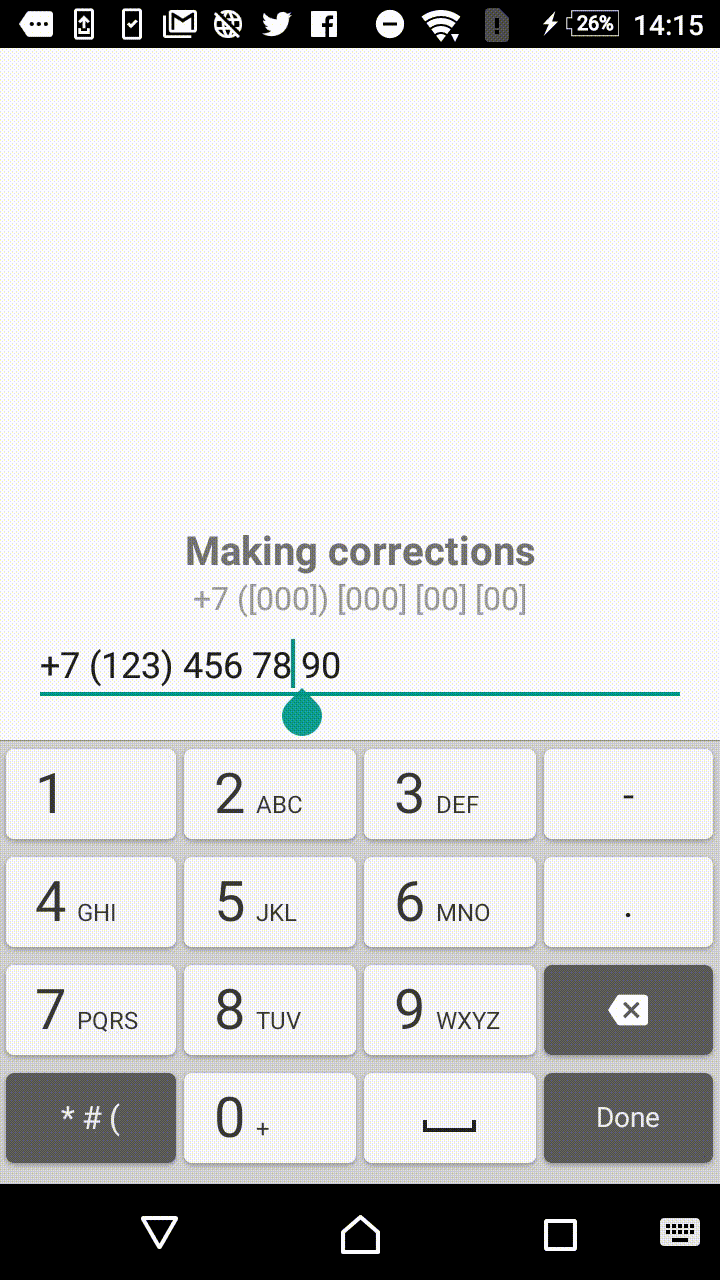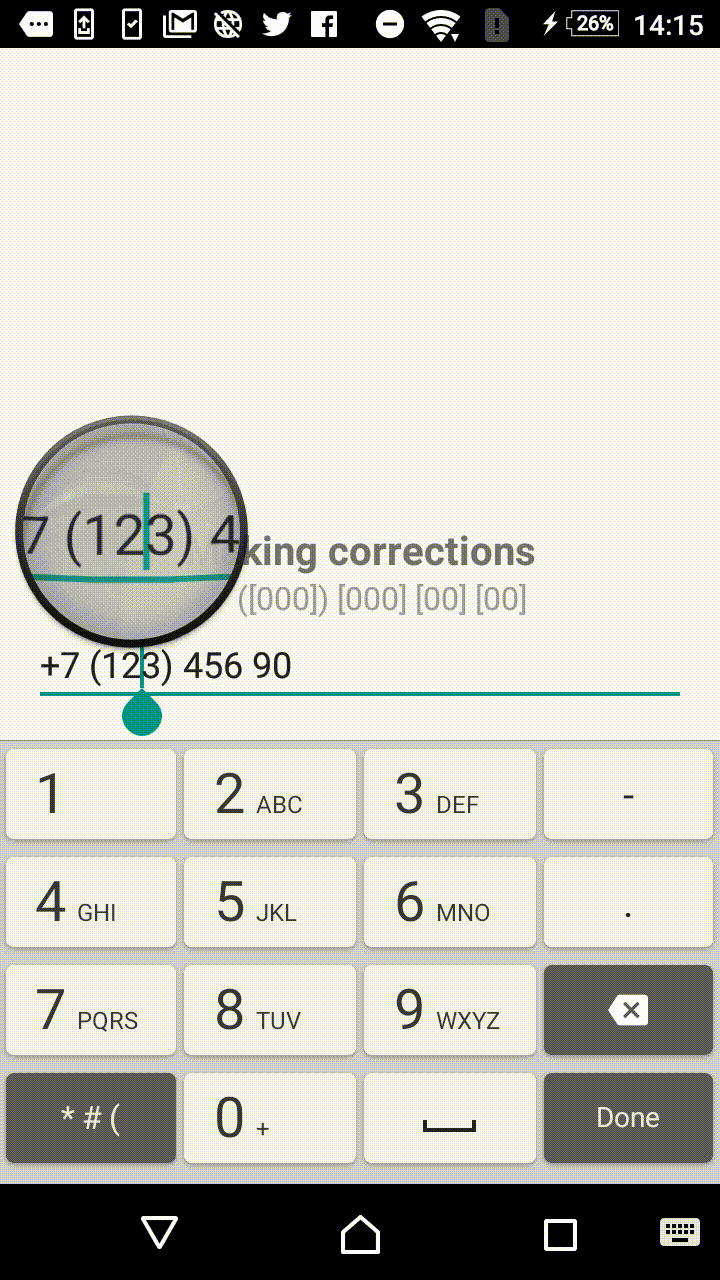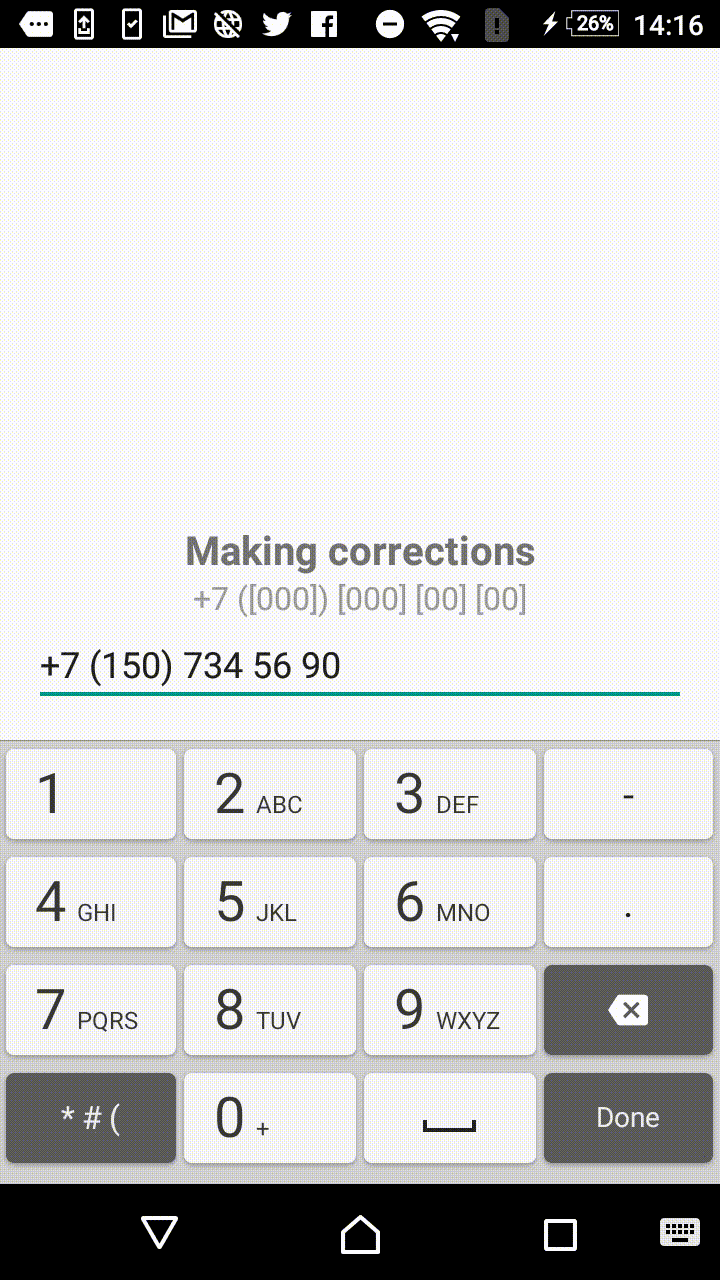
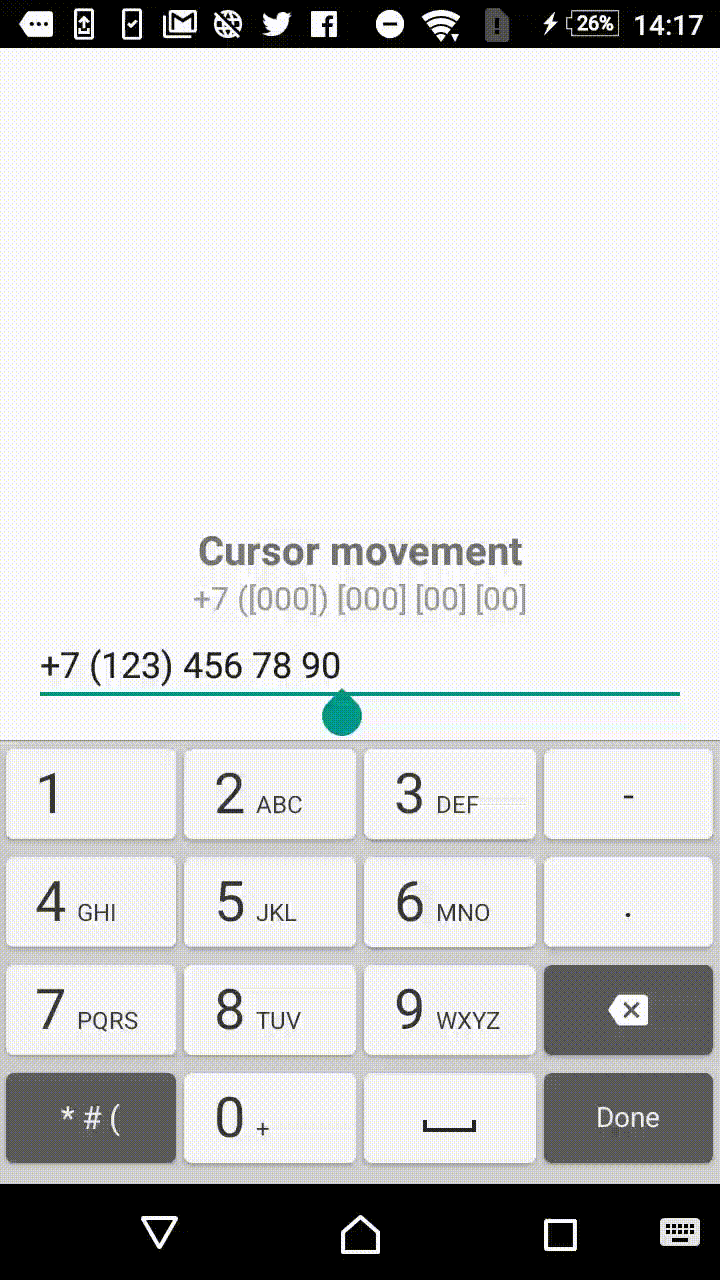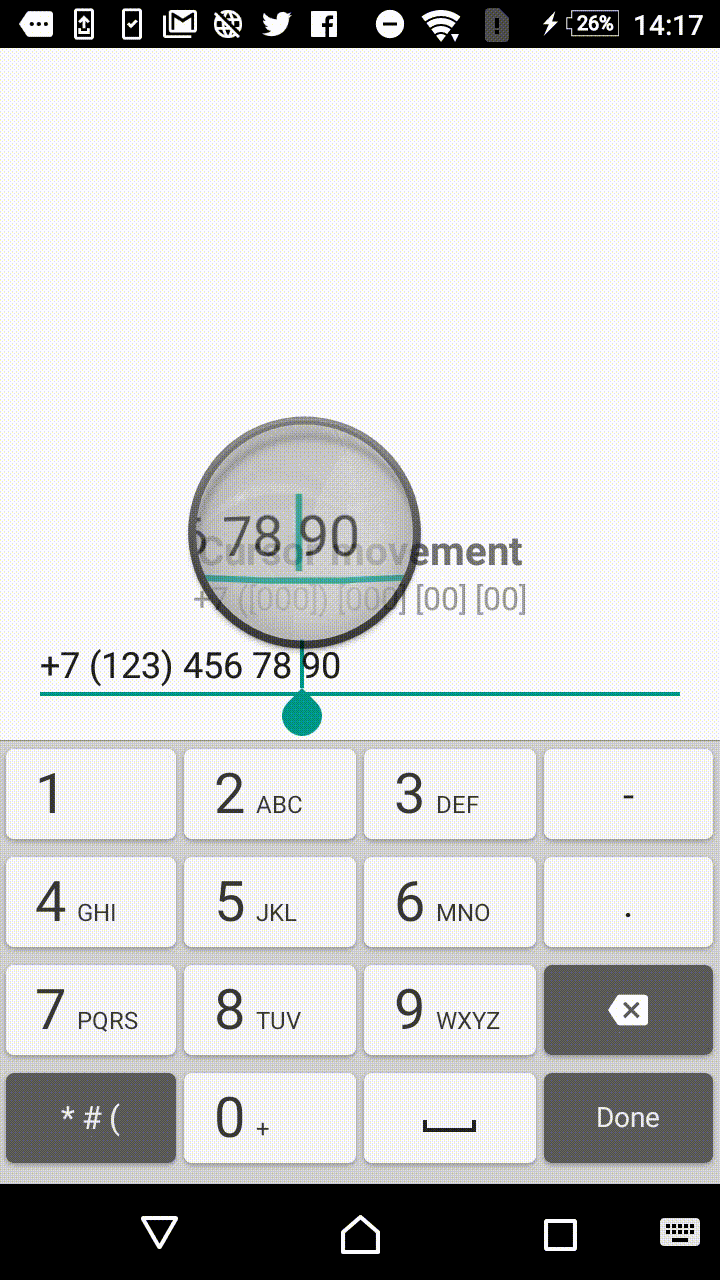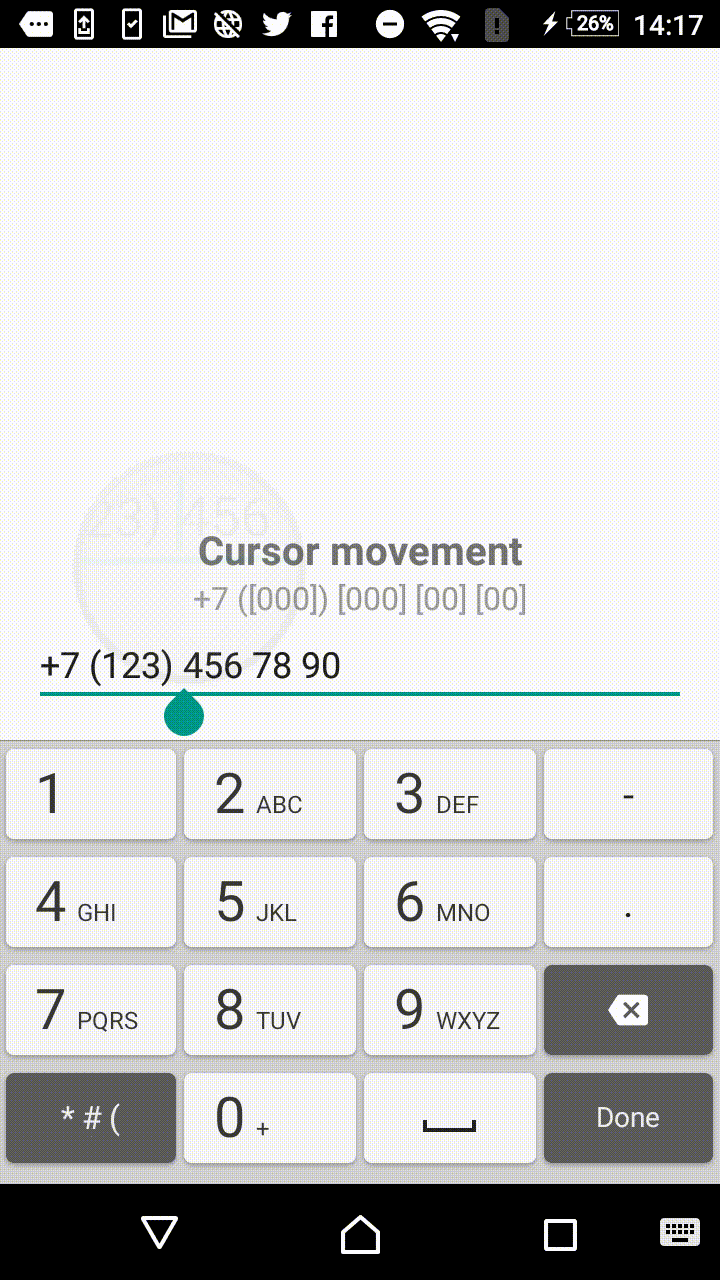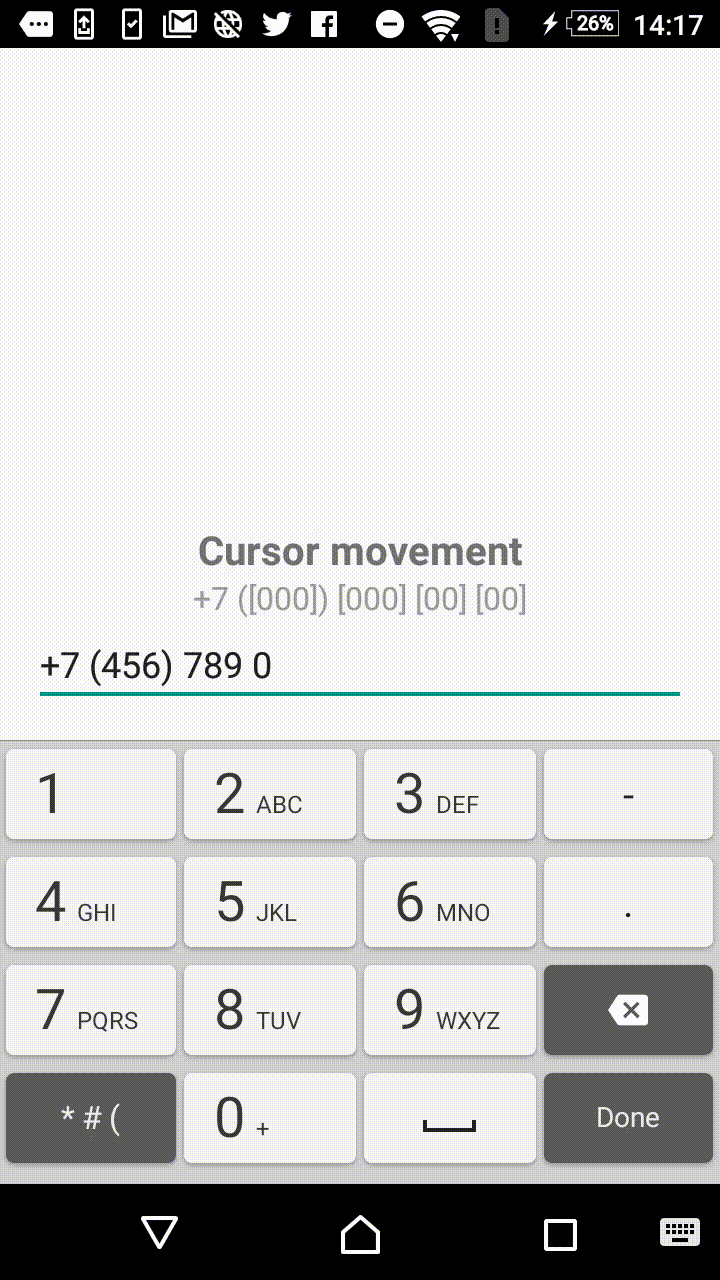
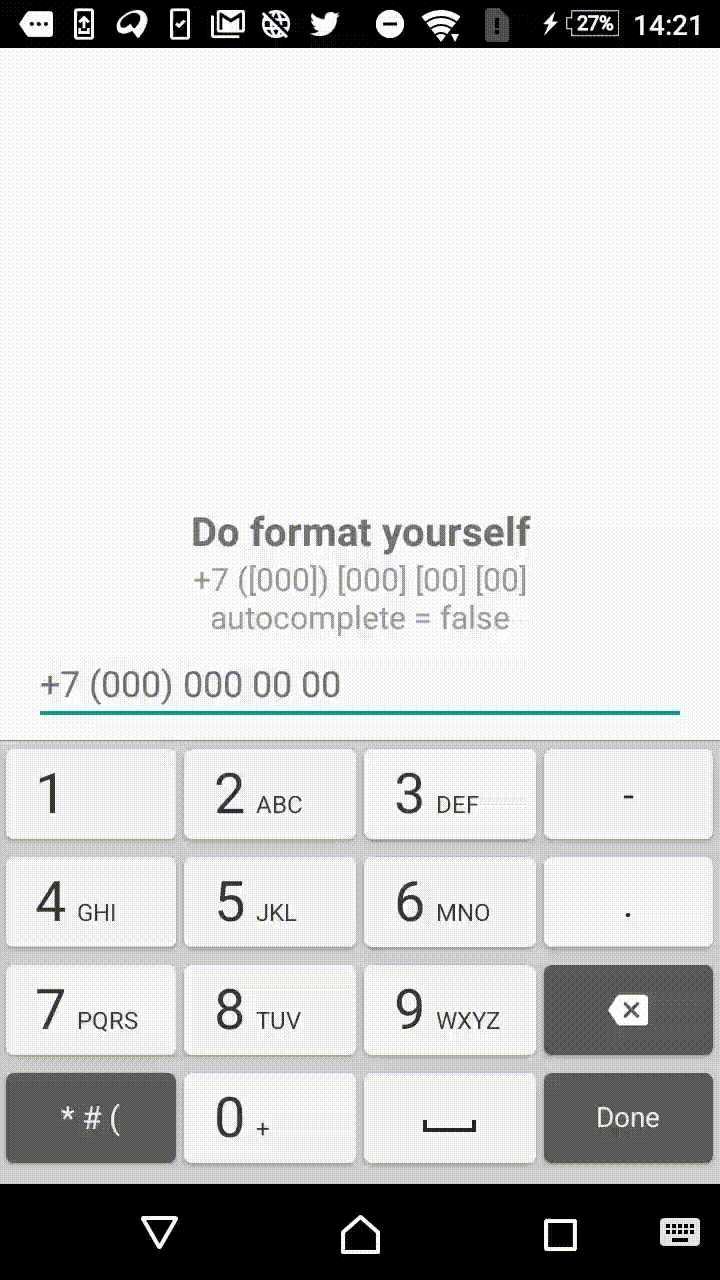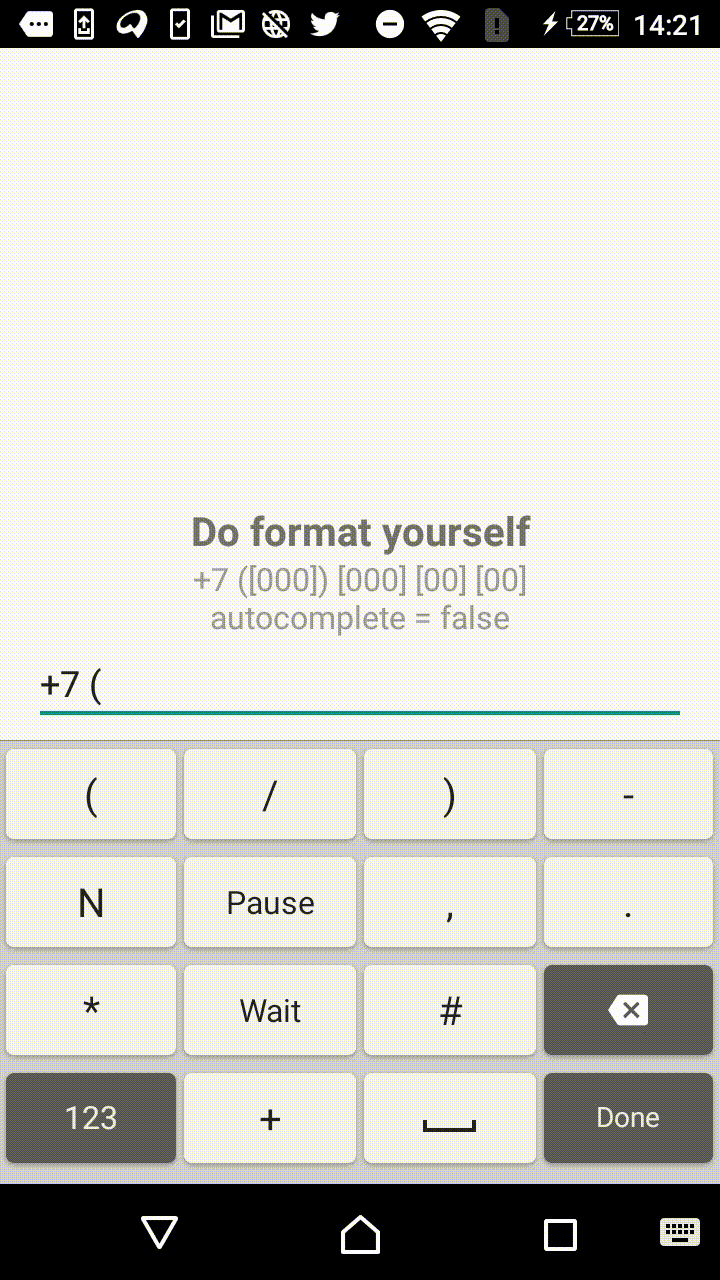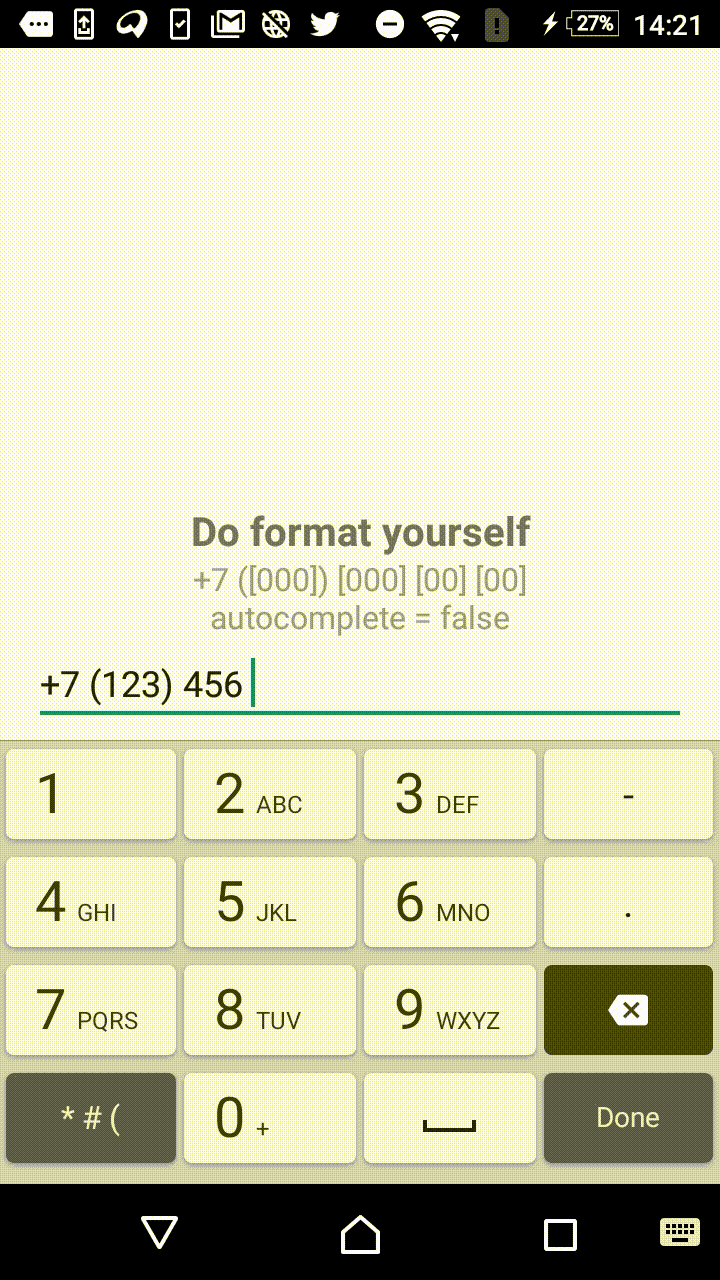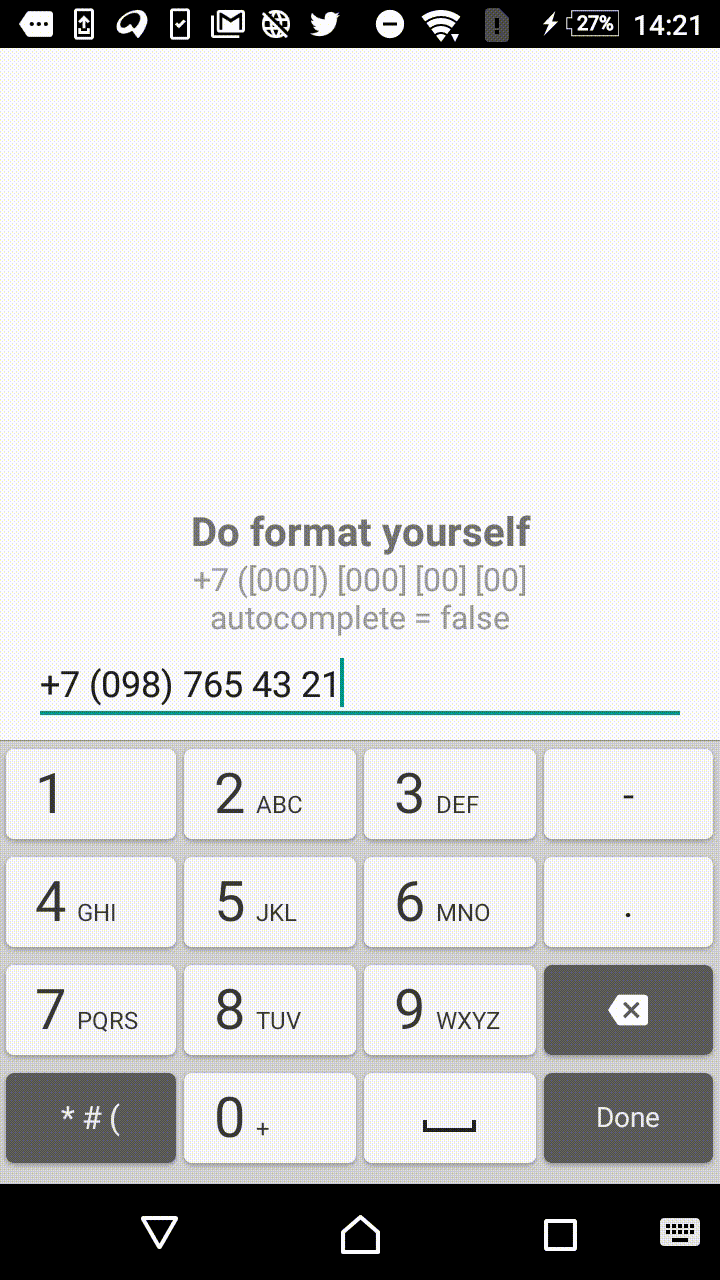
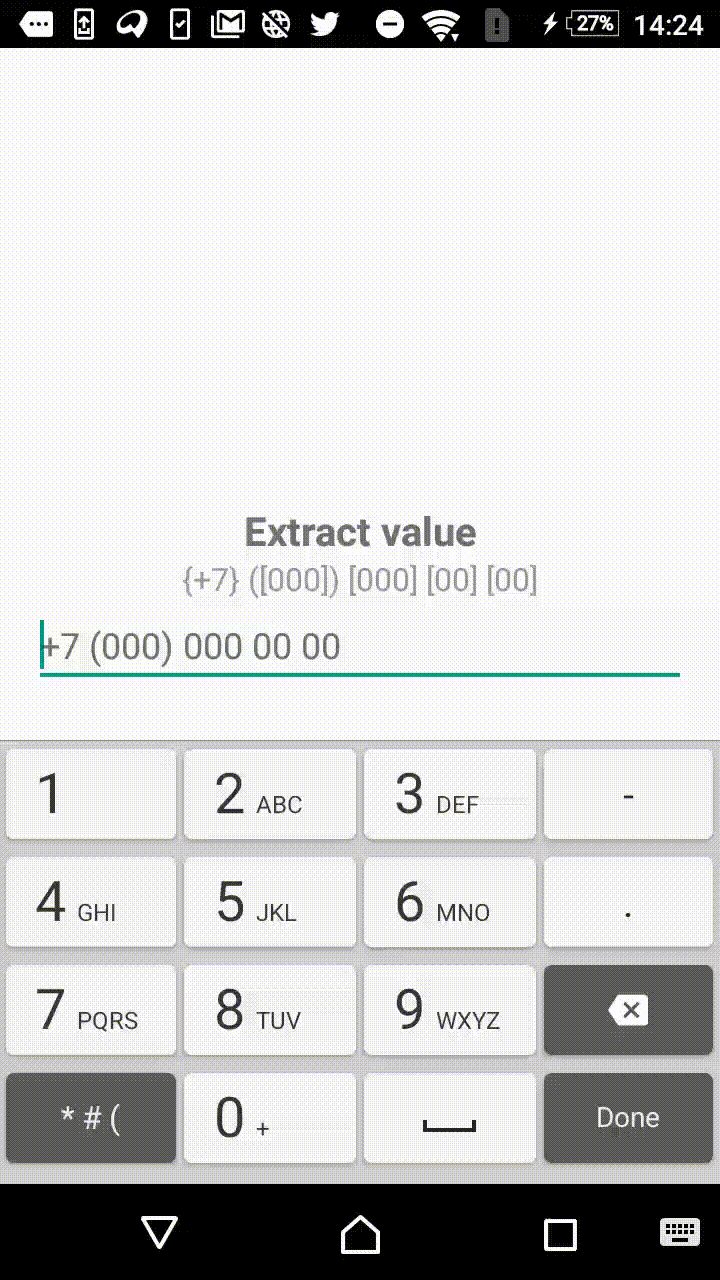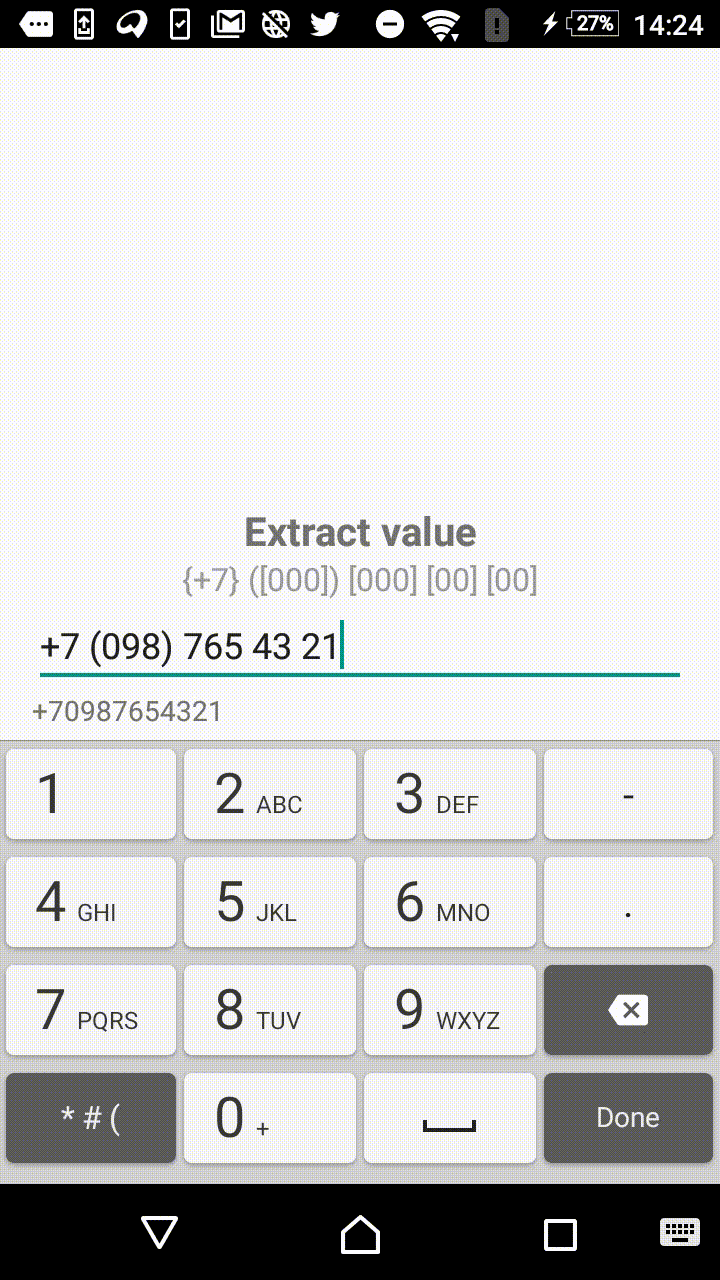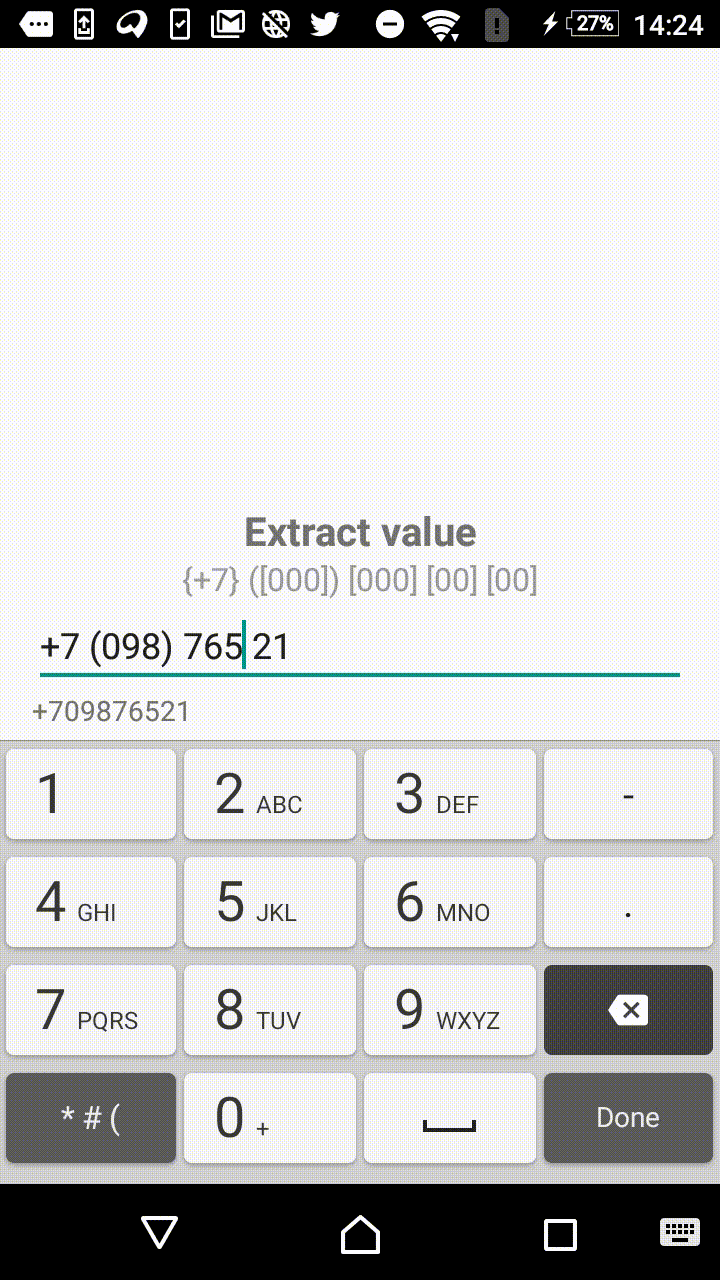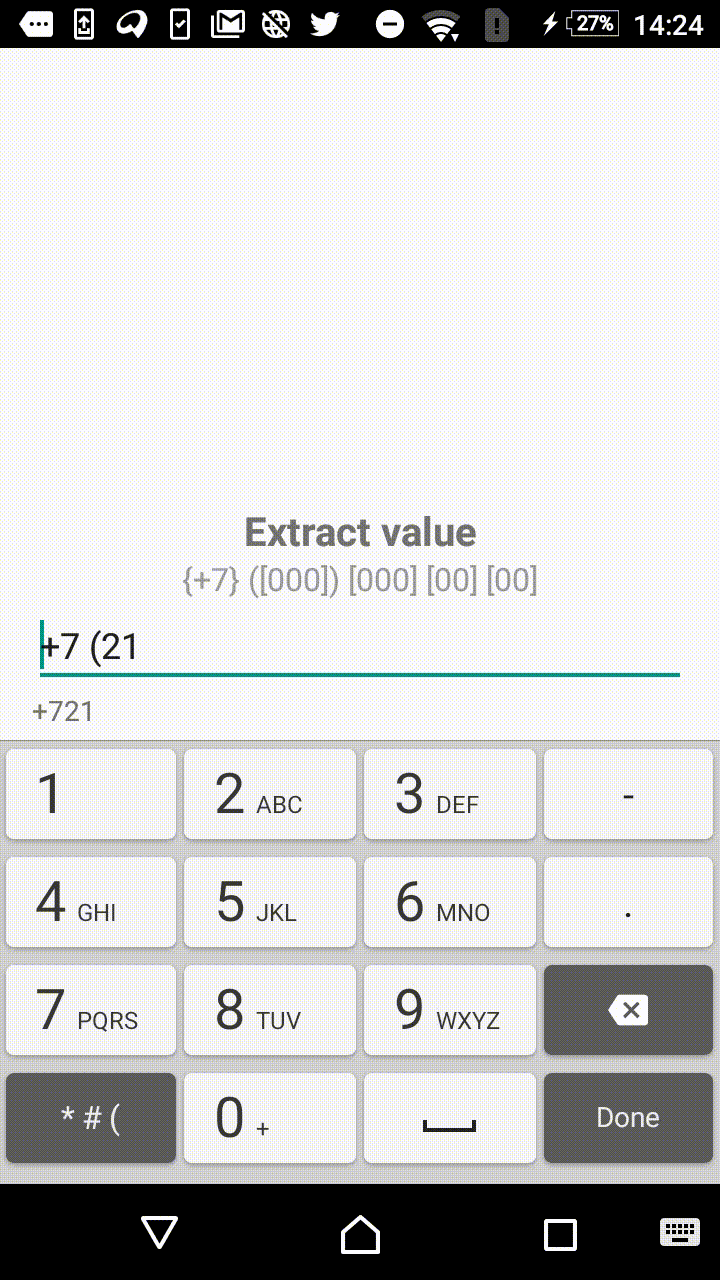
Symbols outside the square brackets will take a place in the output. For instance, +7 ([000]) [000]-[0000] mask will format the input field to the form of +7 (123) 456-7890.
{ }— a block for valueable yet fixed symbols, which could not be altered by the user.
Symbols within the square and curly brackets form an extracted value (valueable characters). In other words, [00]-[00] and [00]{
-
}
[00] will format the input to the same form of 12-34, but in the first case the value, extracted by the library, will be equal to 1234, and in the second case it will result in 12-34.
Mask format examples:
- [00000000000]
- { 401 } -[000]-[00]-[00]
- [000999999]
- { 818 } -[000]-[00]-[00]
- [A][-----------------------------------------------------]
- [A][_______________________________________________________________]
- 8 [0000000000]
- 8([000])[000]-[00]-[00]
- [0000]{ - } [00]
- +1 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]
Installation
Gradle
repositories {
jcenter()
}
dependencies {
compile 'com.redmadrobot:inputmask:2.3.0'
}
Usage
Simple EditText for the phone numbers
Listening to the text change events of EditText and simultaneously altering the entered text could be a bit tricky as long as you need to add, remove and replace symbols intelligently preserving the cursor position.
Thus, the library provides corresponding MaskedTextChangedListener class.
MaskedTextChangedListener conforms to TextWatcher and OnFocusChangeListener interfaces and encaspulates logic to process text edit events. The object might be instantiated via code and then wired with the corresponding EditText.
MaskedTextChangedListener has his own listener MaskedTextChangedListener.ValueListener, which allows capturing extracted value. All the TextWatcher calls from the client EditText are forwarded to the decorated TextWatcher object (you may provide one when initializing MaskedTextChangedListener).
public final class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(final Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text);
final MaskedTextChangedListener listener = new MaskedTextChangedListener(
"+7 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]",
true,
editText,
null,
new MaskedTextChangedListener.ValueListener() {
@Override
public void onTextChanged(boolean maskFilled, @NonNull final String extractedValue) {
Log.d(MainActivity.class.getSimpleName(), extractedValue);
Log.d(MainActivity.class.getSimpleName(), String.valueOf(maskFilled));
}
}
);
editText.addTextChangedListener(listener);
editText.setOnFocusChangeListener(listener);
editText.setHint(listener.placeholder());
}
}
String formatting without views
In case you want to format a String somewhere in your applicaiton's code, Mask is the class you are looking for. Instantiate a Mask instance and feed it with your string, mocking the cursor position:
final Mask mask = new Mask("+7 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]");
final String input = "+71234567890"; final Mask.Result result = mask.apply(
new CaretString(
input,
input.length()
),
true // you may consider disabling autocompletion for your case );
final String output = result.getFormattedText().getString();
Affine masks
An experimental feature. While transforming the text, Mask calculates affinity index, which is basically an Int that shows the absolute rate of similarity between the text and the mask pattern.
This index might be used to choose the most suitable pattern between predefined, and then applied to format the text.
For the implementation, look for the PolyMaskTextChangedListener class, which inherits logic from MaskedTextChangedListener. It has its primary mask pattern and corresponding list of affine formats.
public final class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(final Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_text);
final List<String> affineFormats = new ArrayList<>();
affineFormats.add("8 ([000]) [000] [000] [00]");
final MaskedTextChangedListener listener = new PolyMaskTextChangedListener(
"+7 ([000]) [000] [00] [00]",
affineFormats,
true,
editText,
null,
new MaskedTextChangedListener.ValueListener() {
@Override
public void onTextChanged(boolean maskFilled, @NonNull final String extractedValue) {
Log.d(MainActivity.class.getSimpleName(), extractedValue);
Log.d(MainActivity.class.getSimpleName(), String.valueOf(maskFilled));
}
}
);
editText.addTextChangedListener(listener);
editText.setOnFocusChangeListener(listener);
editText.setHint(listener.placeholder());
}
}
Known issues
InputMask vs. android:inputType
Be careful when specifying field's android:inputType. The library uses native Editable variable received on afterTextChange event in order to replace text efficiently. Because of that, field's inputType is actually considered when the library is trying to mutate the text.
For instance, having a field with android:inputType="numeric", you cannot put spaces and dashes into the mentioned Editable variable by default. Doing so will cause an out of range exception when the MaskedTextChangedListener will try to reposition the cursor.
Still, you may use a workaround by putting the android:digits value beside your android:inputType; there, you should specify all the acceptable symbols:
<EditText
android:inputType="number"
android:digits="0123456789 -."
... />— such that, you'll have the SDK satisfied.
Alternatively, if you are using a programmatic approach without XML files, you may consider configuring a KeyListener like this:
editText.setInputType(InputType.TYPE_CLASS_NUMBER);
editText.setKeyListener(DigitsKeyListener.getInstance("0123456789 -."));
// modify character set for your case, e.g. add "+()"InputMask vs. autocorrection & prediction
Symptoms:
- You've got a wildcard template like
[________], allowing user to write any kind of symbols; - Cursor jumpes to the beggining of the line or to some random position while user input.
In this case text autocorrection & prediction might be a root cause of your problem, as it behaves somewhat weirdly in case when field listener tries to change the text during user input.
If so, consider disabling text suggestions by using corresponding input type:
<EditText
...
android:inputType="textNoSuggestions" />Additionally be aware that some of the third-party keyboards ignore textNoSuggestions setting; the recommendation is to use an extra workaround by setting the inputType to textVisiblePassword.
Compatibility with 1.1.0 and above
In 2.0.0 version separate callbacks onExtracted(String value) onMandatoryCharactersFilled(boolean complete) have been merged into the single callback onTextChanged(boolean maskFilled, @NonNull final String extractedValue)
Be careful while updating dependencies!
License
The library is distributed under the MIT LICENSE.