SmartGL for Android
SmartGL is a Graphic Engine for creating Android Games and Apps. It is based on OpenGL and handles 2D Sprites and 3D Textured Objects.
SmartGL is used by several games and apps.
How to use
The scene is displayed inside a SmartGLView.
A SmartGLViewController interface is used to handle the scene (like adding objects to the scene).
A SmartGLRenderer is used to render the scene in the view.
<fr.arnaudguyon.smartgl.opengl.SmartGLView
android:id="@+id/smartGLView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />You can create an instance of SmartGLViewController or just implement it in your Activity or Fragment.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SmartGLViewController {
private SmartGLView mSmartGLView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mSmartGLView = (SmartGLView) findViewById(R.id.smartGLView);
mSmartGLView.setDefaultRenderer(this);
mSmartGLView.setController(this);
}
}
When the SmartGLView is ready, onPrepareView(...) is called on the SmartGLViewController. This method is the best place to prepare the scene (load textures, and add objects to the scene).
When the SmartGLView is dismissed, onReleaseView(...) is called. This is the best place to release content from memory (textures must be released).
If the View is resized for any reason (rotation of the device for example), onResizeView(...) is called.
At every OpenGL frame, onTick(...) is called.
Finally, every touch interaction calls onTouchEvent(...)
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SmartGLViewController {
@Override
public void onPrepareView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
}
@Override
public void onReleaseView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
}
@Override
public void onResizeView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
}
@Override
public void onTick(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
}
@Override
public void onTouchEvent(SmartGLView smartGLView, TouchHelperEvent event) {
}
}
LifeCycle
It is really important to inform the SmartGLView when the Activity or Fragment is paused or resumed. If you miss this step the scene will not be initialized or restored correctly.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SmartGLViewController {
@Override
protected void onPause() {
if (mSmartGLView != null) {
mSmartGLView.onPause();
}
super.onPause();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
if (mSmartGLView != null) {
mSmartGLView.onResume();
}
}
}
Playing with the Sprites
The draw pipeline includes Render passes. For example you can have several 3D objects in the background pass, and several Sprites in the forground pass.
Let's start with a simple Sprite using a Texture (picture) loaded from the Android drawables. It is highly recommended to share the same texture between several Sprites or Objects 3D when possible: the textures are loaded into the GPU memory and it is often not that big.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SmartGLViewController {
private Texture mSpriteTexture;
@Override
public void onPrepareView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
SmartGLRenderer renderer = smartGLView.getSmartGLRenderer();
RenderPassSprite renderPassSprite = new RenderPassSprite();
renderer.addRenderPass(renderPassSprite);
// add it only once for all Sprites
mSpriteTexture = new Texture(context, R.drawable.planet);
mSprite = new Sprite(120, 120);
// 120 x 120 pixels
mSprite.setPivot(0.5f, 0.5f);
// set position / rotation axis to the middle of the sprite
mSprite.setPos(60, 60);
mSprite.setTexture(mSpriteTexture);
renderPassSprite.addSprite(mSprite);
}
@Override
public void onReleaseView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
if (mSpriteTexture != null) {
mSpriteTexture.release();
}
}
}
Congratulations! The Sprite is displayed on your screen!
Add movement
Let's add some basic moves.
Framerate vary on devices. This is why you should always take the frame duration into account when moving elements on screen.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SmartGLViewController {
@Override
public void onTick(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
SmartGLRenderer renderer = smartGLView.getSmartGLRenderer();
float frameDuration = renderer.getFrameDuration();
if (mSprite != null) {
float newX = mSprite.getPosX() + (frameDuration * 100);
float newY = mSprite.getPosY();
if (newX > 600) {
newX = 0;
}
mSprite.setPos(newX, newY);
float newRot = mSprite.getRotation() + (frameDuration * 100);
mSprite.setRotation(newRot);
}
}
Your Sprite is now moving and rotating on the screen!
Playing with 3D Objects
Now let's add a moving 3D Object! There is a WavefrontModel class that can load a Wavefront model from an .obj file.
See eventually Wave Front format on Wikipedia for the file format definition.
A WavefrontModel.Builder is used to load the model and convert it into a Object3D. For each material used in the model, you will have to assign a corresponding Texture (see AddTexture() method).
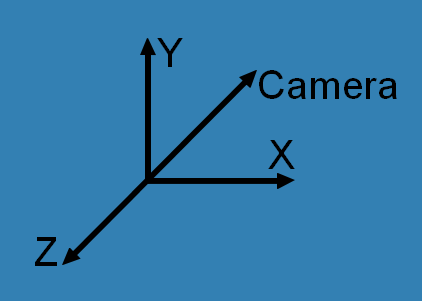
There is no standard unity for the size of the models, so when you load different models you'll probably have to scale them so that they look the correct size compared to each other. You can use setScale() for that. The Camera is set at position (0,0,0) by default, and looking to -Z direction. If you want your objects visible for the camera, you need to put them in front of it, using something like setPos(0,0,-10). You can also move and rotate the camera if you want.
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SmartGLViewController {
private Object3D mSpaceship;
private Texture mShipTexture;
@Override
public void onPrepareView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
// ...
RenderPassObject3D renderPassObject3D = new RenderPassObject3D();
renderer.addRenderPass(renderPassObject3D);
// add it only once for all 3D Objects
mShipTexture = new Texture(context, R.drawable.ship_picture);
WavefrontModel model = new WavefrontModel.Builder(context, R.raw.spaceship_obj)
.addTexture("Material001", mShipTexture) // "Material001" is defined in the spaceship_obj file
.create();
mSpaceship = model.toObject3D();
mSpaceship.setScale(0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);
// Adjust the scale if object is too big / too small
mSpaceship.setPos(0, 0, -5);
// move the object in front of the camera
renderPassObject3D.addObject(mSpaceship);
}
@Override
public void onTick(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
// ...
// add some rotation movement
if (mSpaceship != null) {
float rx = mSpaceship.getRotX() + 100*frameDuration;
float ry = mSpaceship.getRotY() + 77*frameDuration;
float rz = mSpaceship.getRotZ() + 56*frameDuration;
mSpaceship.setRotation(rx, ry, rz);
}
@Override
public void onReleaseView(SmartGLView smartGLView) {
if (mShipTexture != null) {
mShipTexture.release();
}
}
}
}
Congratulations! You know how to display and move Sprites and 3D Objects!
Advanced use of SmartGL
Read the ADVANCED DOCUMENTATION ON WIKI
Samples
See the sample app for a complete implementation (download or clone the repository)
You can also have a look to these apps that use smartGL:
- ZenDay, a 3D Calendar and Task manager
- Slippy Slope, a funny game which uses a lot 2D Sprites
- Bulldozer Rampage, a race game which uses 3D objects
- Time Shift a demo that combines 2D and 3D effects
Installation with gradle
Add the following maven{ } line to your PROJECT build.gradle file
allprojects {
repositories {
jcenter()
maven {
url "https://jitpack.io"
}
// add this line
}
}
Add the libary dependency to your APP build.gradle file
dependencies {
compile 'com.github.smart-fun:smartGL:1.1.4'
// add this line
}
License
Copyright 2016 Arnaud Guyon
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.