Satellite [NO LONGER DEVELOPED]
See Phlux for a better option
Satellite is a simple (for those who are familiar with RxJava) Android library, which allows to properly connect background tasks with visual parts of an application.
Introduction
If you've already seen my Nucleus library: Satellite is basically the same but is much simpler because it does NOT utilize the MVP pattern to do the same job.
Problem
There are some defects in our Android applications and because of these defects we can not call our application reliable:
- An application is unable to continue a background task execution after a configuration change.
And, if a developer is smart enough to handle the previous problem, there is a second one:
- An application does not automatically restart a background task after a process restart. I'm not talking here about an application restart. A process restart is an event that happens randomly with applications that are in the background, in which case the entire application gets killed and after that its activities get restored from the saved state, while all background tasks and static variables do not exist.
While most applications work without such capabilities, their absence is an obvious bug that just sits there and waits for a user who pressed "Login" button while being in a subway and switched to another application because his network connection was too slow. Bugs that almost any application produce in such cases are numerous.
Android docs are covering these problems very briefly, take a look at: Processes and Threads - 4. Background process "If an activity implements its lifecycle methods correctly, and saves its current state, killing its process will not have a visible effect on the user experience, because when the user navigates back to the activity, the activity restores all of its visible state."
This is not true - there WILL be a visible effect because we're not restoring background tasks. The application will restore it's visual state, but it will forget what it is doing. So, if an application restores a progress bar, but does not restore the background task itself - a user will see the usual "progress bar forever" bug.
Satellite
-
In case of a configuration change Satellite automatically re-connects all running background tasks to the new Activity/Fragment/View instance. The application will not forget what it is doing.
-
In case of a process restart Satellite automatically restarts background tasks that are associated with the restored activity. Even when running on a low memory device or waiting for a long running background task completion, the application is still reliable.
-
The entire library has been built keeping The Kiss Principle in mind. Anyone who is familiar with RxJava can read and understand it easily.
-
The library is extremely tiny.
Architecture
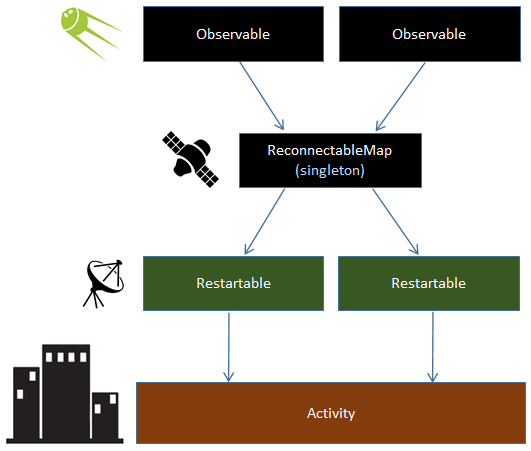
Satellite is better to understand with cosmic analogies. Reactive satellites are awesome. :)
Observable resides in the background. It is out of reach of lifecycle events. All emissions are automatically transformed into Notification<.<T> to make is possible to reuse RxJava chains. onComplete emissions get suppressed. Such way of handling emissions is called channel here.
ReconnectableMap is a singleton which keeps track of all launched observables. It connects them with activities and fragments, providing an Observable connection. You don't normally need to use ReconnectableMap directly, but it is good to know about it. Sometimes you will want to get some debug information from its keys() method.
There is Restartable - this is our land base inside of Activity which manages all the restartable stuff and guarantees that the observable will be completed despite of any lifecycle events.
We also have ObservableFactory interface - we're implementing it to instantiate our satellite code from a given argument. It is a good idea to declare factories outside of Activity to prevent memory leaks during long requests and time consuming operations.
RestartableSet is a set of Restartable that allows to launch more than one observable.
There can be two launch cases: with and without argument. It is recommended to supply arguments in a special Parcelable immutable object ValueMap instead of Bundle. Immutable objects allow to avoid a wide range of problems that can be caused by using mutable data structures. Immutable objects are also reliable enough for multithreading without additional techniques. If you want to go deeper with immutability and the functional juice on Android, take a look at Solid and AutoParcel libraries.
The code
Here is a typical code that is used to launch restartable requests.
public class SignIn implements ObservableFactory<ValueMap, Boolean> {
public static ValueMap argument(String username, String password) {
return ValueMap.map("username", username, "password", password);
}
@Override
public Observable<Boolean> call(ValueMap in) {
return serverApi.signIn(in.get("username"), in.get("password"))
.observeOn(mainThread());
}
}
public class SignInActivity extends BaseActivity {
public static final int CHANNEL_ID = 1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
findViewById(R.id.sign_in)
.setOnClickListener(v -> launch(CHANNEL_ID, SignIn.argument("[email protected]", "***")));
}
@Override
protected Subscription onConnect() {
return new CompositeSubscription(super.onConnect(),
channel(CHANNEL_ID, DeliveryMethod.SINGLE, new SignIn())
.subscribe(split(
value -> log("onNext " + value),
throwable -> log("onError " + throwable))));
}
}
BaseActivity
Unfortunately, Java does not allow us to have multiple inheritance, so the BaseActivity code should be copy/pasted into your project. You can change its code to inherit from AppCompatActivity or any other base Activity you want. There are also BaseFragment and BaseLayout implementations for the same purpose.
split
You may noticed the split magic method. What it does?
All events come from channel method in the materialized state materialize-dematerialize. split dematerializes events and returns them into onNext and onError lambdas.
DeliveryMethod
The DeliveryMethod argument of the channel method is a possibility to say which delivery method should be used to provide values. In example, sometimes you want your value to be delivered a SINGLE time, sometimes you want to receive LATEST updates (and the latest value will be re-delivered on configuration change).
The list of delivery methods is here: DeliveryMethod
Finalize fragments with dismissRestartables()
When a fragment gets detached, it still runs background observables to reattach them during the next attachment or after a configuration change. However, sometimes you want to remove the fragment and all of its background tasks forever. For this scenario there is BaseFragment.dismissRestartables() method.
It is impossible to know when a specific fragment or view gets detached for the last time, so you need to call this cleanup method manually. There is a smart trick which allows to skip this step most of the times: when BaseFragment gets detached, it checks if its activity is finalizing. If it is then it calls dismissRestartables() by itself.
Installation
dependencies {
compile 'info.android15.satellite:satellite:0.4.1'
}
Feedback
Any feedback is welcome. :)